July 29, 2024
Understanding Response Bias: Key Concepts and Applications
What is Response Bias?
Response bias occurs when respondents answer questions in a way that does not accurately reflect their true thoughts or feelings. This can be due to various factors, including social desirability, question wording, and survey conditions.
Common types of response bias include acquiescence bias, social desirability bias, and recall bias.
Theories and Methods Behind Response Bias
Various theories explain the causes and effects of response bias. For example, social desirability theory suggests that respondents may answer questions in a way that they believe is socially acceptable rather than truthful.
Understanding these theories helps researchers design surveys that minimize bias and improve data accuracy.
Examples of Response Bias in Research
Response bias can significantly impact research outcomes. For instance, in customer satisfaction surveys, respondents may overstate their satisfaction to appear polite or avoid confrontation.
Another example is health surveys, where respondents might underreport unhealthy behaviors due to social desirability bias.
Benefits and Challenges of Addressing Response Bias
Benefits
Improves the accuracy and validity of survey data.
Enhances the reliability of research findings.
Enables better decision-making based on accurate data.
Challenges
Identifying and measuring the extent of response bias can be difficult.
Mitigating response bias requires careful survey design and administration.
May involve additional time and resources to implement bias-reduction strategies.
Implementing Effective Response Bias Mitigation Strategies
Effective mitigation of response bias involves designing surveys with clear, neutral wording, ensuring anonymity, and using various methods to cross-validate responses. Training interviewers and pre-testing surveys can also help identify and reduce bias.
By addressing response bias, researchers can improve the quality of their data and the validity of their conclusions.
Key Statistics and Insights About Response Bias
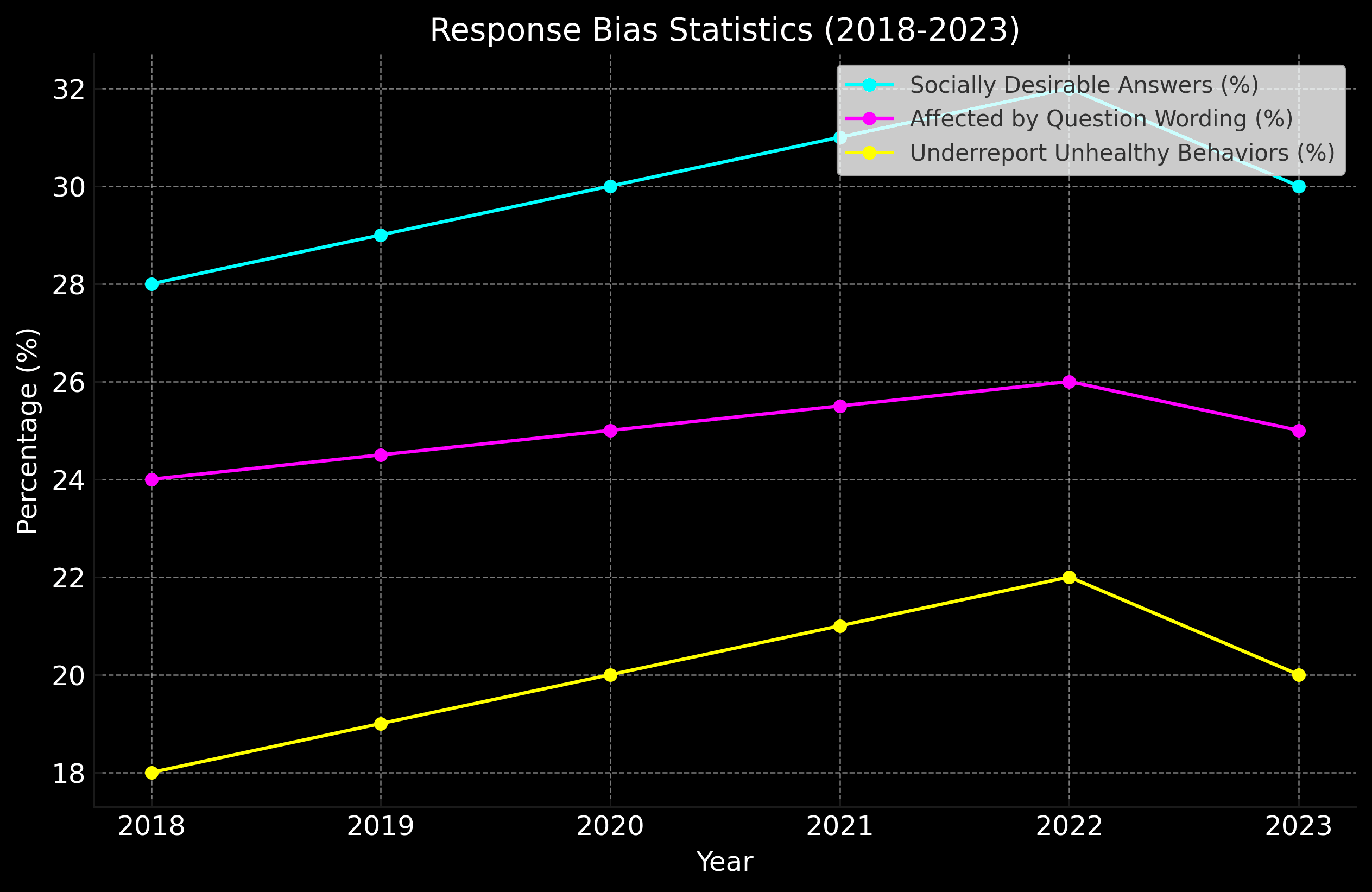
30% of survey respondents admit to giving socially desirable answers
This statistic highlights the prevalence of social desirability bias in survey responses.
25% of survey responses can be affected by question wording
Shows the significant impact of question design on response accuracy.
20% of health survey respondents underreport unhealthy behaviors
Emphasizes the need for careful survey design in sensitive topics like health.
source: NCBI
How Marketing Managers Can Utilize Response Bias Insights
Marketing managers can use insights into response bias to design better customer surveys and improve the accuracy of feedback. By minimizing bias, they can gain more reliable insights into customer preferences and behaviors.
Best Practices for Mitigating Response Bias
First, use neutral and clear question wording. Second, ensure respondent anonymity to encourage honesty.
Third, use multiple methods to cross-validate responses and identify potential biases.
Frequently Asked Questions About Response Bias
How Does Response Bias Affect Research?
Response bias distorts survey data, leading to inaccurate conclusions and potentially flawed decisions based on that data.
By understanding and mitigating response bias, researchers can ensure more reliable and valid results.
What Are the Best Practices for Mitigating Response Bias?
Use clear and neutral question wording, ensure anonymity, and use multiple validation methods.
Pre-testing surveys and training interviewers can also help identify and reduce response bias.
Can Understanding Response Bias Drive Better Business Decisions?
Yes, by improving the accuracy of survey data, businesses can make more informed and effective decisions based on reliable customer insights.
Minimizing response bias helps in understanding true customer preferences and behaviors, enhancing decision-making.